当前我有这样一个NGINX配置
server {
listen 80;
server_name somename alias another.alias;
location / {
root /Users/cai/Desktop/nginx/nginx1;
index index.html index.htm;
}
location /op {
rewrite ^/op/?(.*)$ /$1 break;
root /Users/cai/Desktop/nginx/nginx2;
index index.html index.htm;
}
}
我的期望是,如果我访问的是 localhost,那么帮请求发送到 nginx1下面的静态资源。如果是访问的localhost/op,那么请求发送到nginx2下面的镜头资源。
直白的就是说同一个nginx配置,我期望通过后面的location配置多个静态站点。
这个配置文件是按照我的理解写的,但是在实际使用的时候发现nginx的行为好像并没有按照我的期望去工作。
实际情况是,我如果请求的是localhost/op/ ,那么他会帮我转发到 location / 这个块里面去,很奇怪,排查半天也不知道为何会这样。
最后通过查阅资料发现一个标签叫 alias,可以直接拿来用,甚至不需要去写rewrite。
改进后的配置为:
server {
listen 80;
server_name somename alias another.alias;
location / {
root /Users/cai/Desktop/nginx/nginx1;
index index.html index.htm;
}
location /op {
alias /Users/cai/Desktop/nginx/nginx2;
index index.html index.htm;
}
}
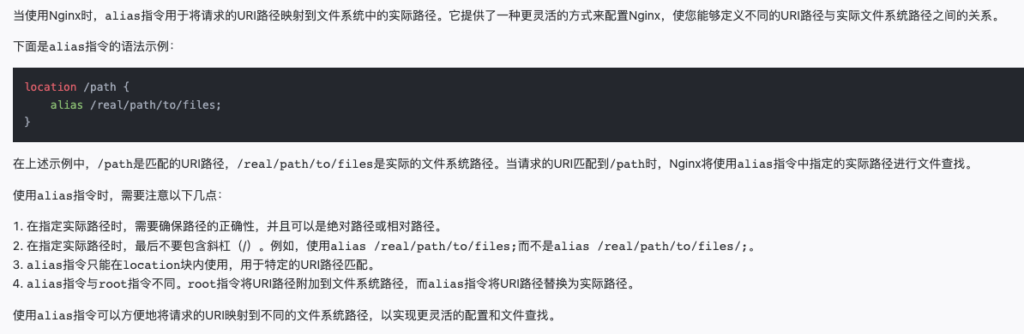
通过官方文档 http://nginx.org/en/docs/http/ngx_http_core_module.html#alias,我们发现alias有这样的行为:
alias定义了一种路径替换规则. 例如,如下配置项目
location /i/ {
alias /data/w3/images/;
}
当请求路径为“/i/top.gif”, 请求就会被转发到文件 /data/w3/images/top.gif 。
后续:
发现如果我请求 localhost/op , nginx会自动帮我重定向到 localhost/op/,如果我的请求带端口的,比如我请求 localhost:3000/op,nginx还是会帮我请求重定向到 localhost/op/。
这就扯淡了啊。。
用下面配置可以解决这个问题:
server {
listen 80;
server_name somename alias another.alias;
location / {
root /Users/cai/Desktop/nginx/nginx1;
index index.html index.htm;
}
location /op {
alias /Users/cai/Desktop/nginx/nginx2;
index index.html index.htm;
try_files $uri $uri/ $uri/index.html =404;
}
}
具体什么原因,还要去研究下。。