1.用String.format拼接字符串
不知道你有没有拼接过字符串,特别是那种有多个参数,字符串比较长的情况。
比如现在有个需求:要用get请求调用第三方接口,url后需要拼接多个参数。
以前我们的请求地址是这样拼接的:
String url = "http://susan.sc.cn?userName="+userName+"&age="+age+"&address="+address+"&sex="+sex+"&roledId="+roleId;
字符串使用+号拼接,非常容易出错。
后面优化了一下,改为使用StringBuilder拼接字符串:
StringBuilder urlBuilder = new StringBuilder("http://susan.sc.cn?");
urlBuilder.append("userName=")
.append(userName)
.append("&age=")
.append(age)
.append("&address=")
.append(address)
.append("&sex=")
.append(sex)
.append("&roledId=")
.append(roledId);
代码优化之后,稍微直观点。
但还是看起来比较别扭。
这时可以使用String.format方法优化:
String requestUrl = "http://susan.sc.cn?userName=%s&age=%s&address=%s&sex=%s&roledId=%s"; String url = String.format(requestUrl,userName,age,address,sex,roledId);
代码的可读性,一下子提升了很多。
我们平常可以使用String.format方法拼接url请求参数,日志打印等字符串。
但不建议在for循环中用它拼接字符串,因为它的执行效率,比使用+号拼接字符串,或者使用StringBuilder拼接字符串都要慢一些。
2.创建可缓冲的IO流
IO流想必大家都使用得比较多,我们经常需要把数据写入某个文件,或者从某个文件中读取数据到内存中,甚至还有可能把文件a,从目录b,复制到目录c下等。
JDK给我们提供了非常丰富的API,可以去操作IO流。
例如:
public class IoTest1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
FileInputStream fis = null;
FileOutputStream fos = null;
try {
File srcFile = new File("/Users/dv_susan/Documents/workspace/jump/src/main/java/com/sue/jump/service/test1/1.txt");
File destFile = new File("/Users/dv_susan/Documents/workspace/jump/src/main/java/com/sue/jump/service/test1/2.txt");
fis = new FileInputStream(srcFile);
fos = new FileOutputStream(destFile);
int len;
while ((len = fis.read()) != -1) {
fos.write(len);
}
fos.flush();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if (fos != null) {
fos.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
if (fis != null) {
fis.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
这个例子主要的功能,是将1.txt文件中的内容复制到2.txt文件中。这例子使用普通的IO流从功能的角度来说,也能满足需求,但性能却不太好。
因为这个例子中,从1.txt文件中读一个字节的数据,就会马上写入2.txt文件中,需要非常频繁的读写文件。
优化:
public class IoTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BufferedInputStream bis = null;
BufferedOutputStream bos = null;
FileInputStream fis = null;
FileOutputStream fos = null;
try {
File srcFile = new File("/Users/dv_susan/Documents/workspace/jump/src/main/java/com/sue/jump/service/test1/1.txt");
File destFile = new File("/Users/dv_susan/Documents/workspace/jump/src/main/java/com/sue/jump/service/test1/2.txt");
fis = new FileInputStream(srcFile);
fos = new FileOutputStream(destFile);
bis = new BufferedInputStream(fis);
bos = new BufferedOutputStream(fos);
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
int len;
while ((len = bis.read(buffer)) != -1) {
bos.write(buffer, 0, len);
}
bos.flush();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if (bos != null) {
bos.close();
}
if (fos != null) {
fos.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
if (bis != null) {
bis.close();
}
if (fis != null) {
fis.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
这个例子使用BufferedInputStream和BufferedOutputStream创建了可缓冲的输入输出流。
最关键的地方是定义了一个buffer字节数组,把从1.txt文件中读取的数据临时保存起来,后面再把该buffer字节数组的数据,一次性批量写入到2.txt中。
这样做的好处是,减少了读写文件的次数,而我们都知道读写文件是非常耗时的操作。也就是说使用可缓存的输入输出流,可以提升IO的性能,特别是遇到文件非常大时,效率会得到显著提升。
3.减少循环次数
在我们日常开发中,循环遍历集合是必不可少的操作。
但如果循环层级比较深,循环中套循环,可能会影响代码的执行效率。
反例:
for(User user: userList) {
for(Role role: roleList) {
if(user.getRoleId().equals(role.getId())) {
user.setRoleName(role.getName());
}
}
}
这个例子中有两层循环,如果userList和roleList数据比较多的话,需要循环遍历很多次,才能获取我们所需要的数据,非常消耗cpu资源。
正例:
Map<Long, List<Role>> roleMap = roleList.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Role::getId));
for (User user : userList) {
List<Role> roles = roleMap.get(user.getRoleId());
if(CollectionUtils.isNotEmpty(roles)) {
user.setRoleName(roles.get(0).getName());
}
}
减少循环次数,最简单的办法是,把第二层循环的集合变成map,这样可以直接通过key,获取想要的value数据。
虽说map的key存在hash冲突的情况,但遍历存放数据的链表或者红黑树的时间复杂度,比遍历整个list集合要小很多。
4.用完资源记得及时关闭
在我们日常开发中,可能经常访问资源,比如:获取数据库连接,读取文件等。
我们以获取数据库连接为例。
反例:
//1. 加载驱动类
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
//2. 创建连接
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql//localhost:3306/db?allowMultiQueries=true&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8","root","123456");
//3.编写sql
String sql ="select * from user";
//4.创建PreparedStatement
PreparedStatement pstmt = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
//5.获取查询结果
ResultSet rs = pstmt.execteQuery();
while(rs.next()){
int id = rs.getInt("id");
String name = rs.getString("name");
}
上面这段代码可以正常运行,但却犯了一个很大的错误,即:ResultSet、PreparedStatement和Connection对象的资源,使用完之后,没有关闭。
我们都知道,数据库连接是非常宝贵的资源。我们不可能一直创建连接,并且用完之后,也不回收,白白浪费数据库资源。
正例:
//1. 加载驱动类
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement pstmt = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
try {
//2. 创建连接
connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql//localhost:3306/db?allowMultiQueries=true&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8","root","123456");
//3.编写sql
String sql ="select * from user";
//4.创建PreparedStatement
pstmt = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
//5.获取查询结果
rs = pstmt.execteQuery();
while(rs.next()){
int id = rs.getInt("id");
String name = rs.getString("name");
}
} catch(Exception e) {
log.error(e.getMessage(),e);
} finally {
if(rs != null) {
rs.close();
}
if(pstmt != null) {
pstmt.close();
}
if(connection != null) {
connection.close();
}
}
这个例子中,无论是ResultSet,或者PreparedStatement,还是Connection对象,使用完之后,都会调用close方法关闭资源。
在这里温馨提醒一句:ResultSet,或者PreparedStatement,还是Connection对象,这三者关闭资源的顺序不能反了,不然可能会出现异常。
5.使用池技术
我们都知道,从数据库查数据,首先要连接数据库,获取Connection资源。
想让程序多线程执行,需要使用Thread类创建线程,线程也是一种资源。
通常一次数据库操作的过程是这样的:
- 创建连接
- 进行数据库操作
- 关闭连接
而创建连接和关闭连接,是非常耗时的操作,创建连接需要同时会创建一些资源,关闭连接时,需要回收那些资源。
如果用户的每一次数据库请求,程序都都需要去创建连接和关闭连接的话,可能会浪费大量的时间。
此外,可能会导致数据库连接过多。
我们都知道数据库的最大连接数是有限的,以mysql为例,最大连接数是:100,不过可以通过参数调整这个数量。
如果用户请求的连接数超过最大连接数,就会报:too many connections异常。如果有新的请求过来,会发现数据库变得不可用。
这时可以通过命令:
show variables like max_connections
查看最大连接数。
然后通过命令:
set GLOBAL max_connections=1000
手动修改最大连接数。
这种做法只能暂时缓解问题,不是一个好的方案,无法从根本上解决问题。
最大的问题是:数据库连接数可以无限增长,不受控制。
这时我们可以使用数据库连接池。
目前Java开源的数据库连接池有:
- DBCP:是一个依赖Jakarta commons-pool对象池机制的数据库连接池。
- C3P0:是一个开放源代码的JDBC连接池,它在lib目录中与Hibernate一起发布,包括了实现jdbc3和jdbc2扩展规范说明的Connection 和Statement 池的DataSources 对象。
- Druid:阿里的Druid,不仅是一个数据库连接池,还包含一个ProxyDriver、一系列内置的JDBC组件库、一个SQL Parser。
- Proxool:是一个Java SQL Driver驱动程序,它提供了对选择的其它类型的驱动程序的连接池封装,可以非常简单的移植到已有代码中。
目前用的最多的数据库连接池是:Druid。
6.反射时加缓存
我们都知道通过反射创建对象实例,比使用new关键字要慢很多。
由此,不太建议在用户请求过来时,每次都通过反射实时创建实例。
有时候,为了代码的灵活性,又不得不用反射创建实例,这时该怎么办呢?
答:加缓存。
其实spring中就使用了大量的反射,我们以支付方法为例。
根据前端传入不同的支付code,动态找到对应的支付方法,发起支付。
我们先定义一个注解。
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
public @interface PayCode {
String value();
String name();
}
在所有的支付类上都加上该注解
@PayCode(value = "alia", name = "支付宝支付")
@Service
public class AliaPay implements IPay {
@Override
public void pay() {
System.out.println("===发起支付宝支付===");
}
}
@PayCode(value = "weixin", name = "微信支付")
@Service
public class WeixinPay implements IPay {
@Override
public void pay() {
System.out.println("===发起微信支付===");
}
}
@PayCode(value = "jingdong", name = "京东支付")
@Service
public class JingDongPay implements IPay {
@Override
public void pay() {
System.out.println("===发起京东支付===");
}
}
然后增加最关键的类:
@Service
public class PayService2 implements ApplicationListener<ContextRefreshedEvent> {
private static Map<String, IPay> payMap = null;
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(ContextRefreshedEvent contextRefreshedEvent) {
ApplicationContext applicationContext = contextRefreshedEvent.getApplicationContext();
Map<String, Object> beansWithAnnotation = applicationContext.getBeansWithAnnotation(PayCode.class);
if (beansWithAnnotation != null) {
payMap = new HashMap<>();
beansWithAnnotation.forEach((key, value) ->{
String bizType = value.getClass().getAnnotation(PayCode.class).value();
payMap.put(bizType, (IPay) value);
});
}
}
public void pay(String code) {
payMap.get(code).pay();
}
}
PayService2类实现了ApplicationListener接口,这样在onApplicationEvent方法中,就可以拿到ApplicationContext的实例。这一步,其实是在spring容器启动的时候,spring通过反射我们处理好了。
我们再获取打了PayCode注解的类,放到一个map中,map中的key就是PayCode注解中定义的value,跟code参数一致,value是支付类的实例。
这样,每次就可以每次直接通过code获取支付类实例,而不用if…else判断了。如果要加新的支付方法,只需在支付类上面打上PayCode注解定义一个新的code即可。
注意:这种方式的code可以没有业务含义,可以是纯数字,只要不重复就行。
7.多线程处理
很多时候,我们需要在某个接口中,调用其他服务的接口。
比如有这样的业务场景:
在用户信息查询接口中需要返回:用户名称、性别、等级、头像、积分、成长值等信息。
而用户名称、性别、等级、头像在用户服务中,积分在积分服务中,成长值在成长值服务中。为了汇总这些数据统一返回,需要另外提供一个对外接口服务。
于是,用户信息查询接口需要调用用户查询接口、积分查询接口 和 成长值查询接口,然后汇总数据统一返回。
调用过程如下图所示:
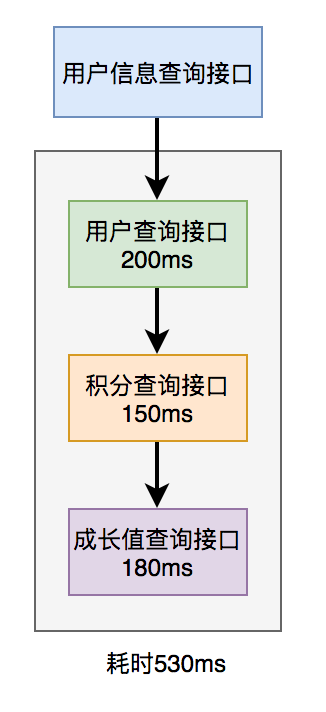
调用远程接口总耗时 530ms = 200ms + 150ms + 180ms
显然这种串行调用远程接口性能是非常不好的,调用远程接口总的耗时为所有的远程接口耗时之和。
那么如何优化远程接口性能呢?
上面说到,既然串行调用多个远程接口性能很差,为什么不改成并行呢?
如下图所示:
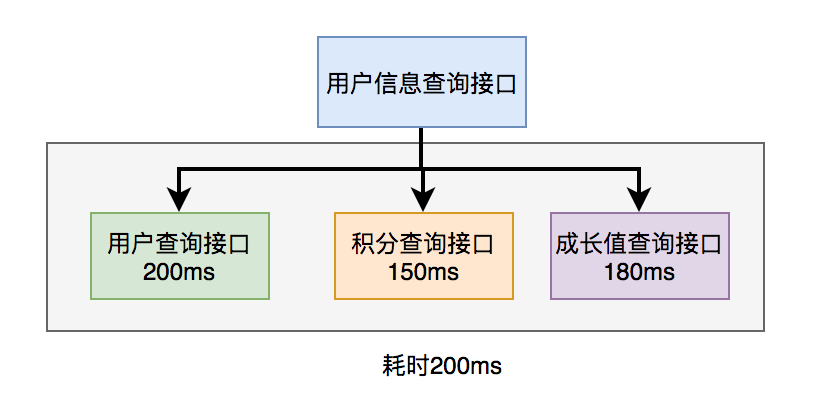
调用远程接口总耗时 200ms = 200ms(即耗时最长的那次远程接口调用)
在java8之前可以通过实现Callable接口,获取线程返回结果。
java8以后通过CompleteFuture类实现该功能。我们这里以CompleteFuture为例:
public UserInfo getUserInfo(Long id) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
final UserInfo userInfo = new UserInfo();
CompletableFuture userFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
getRemoteUserAndFill(id, userInfo);
return Boolean.TRUE;
}, executor);
CompletableFuture bonusFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
getRemoteBonusAndFill(id, userInfo);
return Boolean.TRUE;
}, executor);
CompletableFuture growthFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
getRemoteGrowthAndFill(id, userInfo);
return Boolean.TRUE;
}, executor);
CompletableFuture.allOf(userFuture, bonusFuture, growthFuture).join();
userFuture.get();
bonusFuture.get();
growthFuture.get();
return userInfo;
}
温馨提醒一下,这两种方式别忘了使用线程池。示例中我用到了executor,表示自定义的线程池,为了防止高并发场景下,出现线程过多的问题。
8.懒加载
有时候,创建对象是一个非常耗时的操作,特别是在该对象的创建过程中,还需要创建很多其他的对象时。
我们以单例模式为例。
在介绍单例模式的时候,必须要先介绍它的两种非常著名的实现方式:饿汉模式 和 懒汉模式。
8.1 饿汉模式
实例在初始化的时候就已经建好了,不管你有没有用到,先建好了再说。具体代码如下:
public class SimpleSingleton {
//持有自己类的引用
private static final SimpleSingleton INSTANCE = new SimpleSingleton();
//私有的构造方法
private SimpleSingleton() {
}
//对外提供获取实例的静态方法
public static SimpleSingleton getInstance() {
return INSTANCE;
}
}
使用饿汉模式的好处是:没有线程安全的问题,但带来的坏处也很明显。
private static final SimpleSingleton INSTANCE = new SimpleSingleton();
一开始就实例化对象了,如果实例化过程非常耗时,并且最后这个对象没有被使用,不是白白造成资源浪费吗?
还真是啊。
这个时候你也许会想到,不用提前实例化对象,在真正使用的时候再实例化不就可以了?
这就是我接下来要介绍的:懒汉模式。
8.2 懒汉模式
顾名思义就是实例在用到的时候才去创建,“比较懒”,用的时候才去检查有没有实例,如果有则返回,没有则新建。具体代码如下:
public class SimpleSingleton2 {
private static SimpleSingleton2 INSTANCE;
private SimpleSingleton2() {
}
public static SimpleSingleton2 getInstance() {
if (INSTANCE == null) {
INSTANCE = new SimpleSingleton2();
}
return INSTANCE;
}
}
示例中的INSTANCE对象一开始是空的,在调用getInstance方法才会真正实例化。
懒汉模式相对于饿汉模式,没有提前实例化对象,在真正使用的时候再实例化,在实例化对象的阶段效率更高一些。
除了单例模式之外,懒加载的思想,使用比较多的可能是:
- spring的@Lazy注解。在spring容器启动的时候,不会调用其getBean方法初始化实例。
- mybatis的懒加载。在mybatis做级联查询的时候,比如查用户的同时需要查角色信息。如果用了懒加载,先只查用户信息,真正使用到角色了,才取查角色信息。
9.初始化集合时指定大小
我们在实际项目开发中,需要经常使用集合,比如:ArrayList、HashMap等。
但有个问题:你在初始化集合时指定了大小的吗?
反例:
public class Test2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
long time1 = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) {
list.add(i);
}
System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis() - time1);
}
}
执行时间:
12
如果在初始化集合时指定了大小。
正例:
public class Test2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Integer> list2 = new ArrayList<>(100000);
long time2 = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) {
list2.add(i);
}
System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis() - time2);
}
}
执行时间:
6
我们惊奇的发现,在创建集合时指定了大小,比没有指定大小,添加10万个元素的效率提升了一倍。
如果你看过ArrayList源码,你就会发现它的默认大小是10,如果添加元素超过了一定的阀值,会按1.5倍的大小扩容。
你想想,如果装10万条数据,需要扩容多少次呀?而每次扩容都需要不停的复制元素,从老集合复制到新集合中,需要浪费多少时间呀。
10.不要满屏try…catch异常
以前我们在开发接口时,如果出现异常,为了给用户一个更友好的提示,例如:
@RequestMapping("/test")
@RestController
public class TestController {
@GetMapping("/add")
public String add() {
int a = 10 / 0;
return "成功";
}
}
如果不做任何处理,当我们请求add接口时,执行结果直接报错:
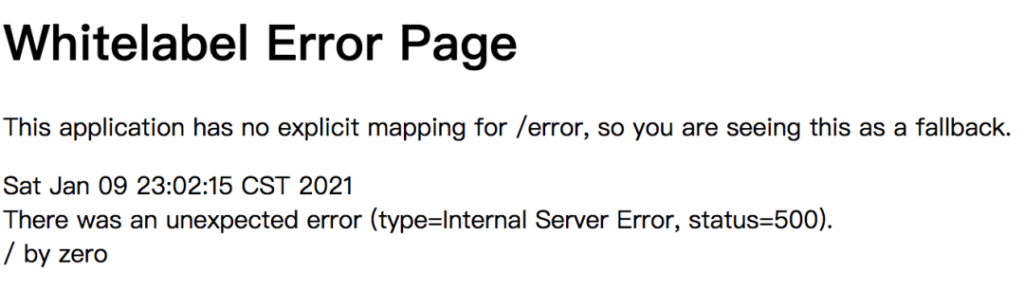
what?用户能直接看到错误信息?
这种交互方式给用户的体验非常差,为了解决这个问题,我们通常会在接口中捕获异常:
@GetMapping("/add")
public String add() {
String result = "成功";
try {
int a = 10 / 0;
} catch (Exception e) {
result = "数据异常";
}
return result;
}
接口改造后,出现异常时会提示:“数据异常”,对用户来说更友好。
看起来挺不错的,但是有问题。。。
如果只是一个接口还好,但是如果项目中有成百上千个接口,都要加上异常捕获代码吗?
答案是否定的,这时全局异常处理就派上用场了:RestControllerAdvice。
@RestControllerAdvice
public class GlobalExceptionHandler {
@ExceptionHandler(Exception.class)
public String handleException(Exception e) {
if (e instanceof ArithmeticException) {
return "数据异常";
}
if (e instanceof Exception) {
return "服务器内部异常";
}
retur nnull;
}
}
只需在handleException方法中处理异常情况,业务接口中可以放心使用,不再需要捕获异常(有人统一处理了)。真是爽歪歪。
11.位运算效率更高
如果你读过JDK的源码,比如:ThreadLocal、HashMap等类,你就会发现,它们的底层都用了位运算。
为什么开发JDK的大神们,都喜欢用位运算?
答:因为位运算的效率更高。
在ThreadLocal的get、set、remove方法中都有这样一行代码:
int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (len-1);
通过key的hashCode值,与数组的长度减1。其中key就是ThreadLocal对象,与数组的长度减1,相当于除以数组的长度减1,然后取模。
这是一种hash算法。
接下来给大家举个例子:假设len=16,key.threadLocalHashCode=31,
于是:int i = 31 & 15 = 15
相当于:int i = 31 % 16 = 15
计算的结果是一样的,但是使用与运算效率跟高一些。
为什么与运算效率更高?
答:因为ThreadLocal的初始大小是16,每次都是按2倍扩容,数组的大小其实一直都是2的n次方。
这种数据有个规律就是高位是0,低位都是1。在做与运算时,可以不用考虑高位,因为与运算的结果必定是0。只需考虑低位的与运算,所以效率更高。
12.巧用第三方工具类
在Java的庞大体系中,其实有很多不错的小工具,也就是我们平常说的:轮子。
如果在我们的日常工作当中,能够将这些轮子用户,再配合一下idea的快捷键,可以极大得提升我们的开发效率。
如果你引入com.google.guava的pom文件,会获得很多好用的小工具。这里推荐一款com.google.common.collect包下的集合工具:Lists。
它是在太好用了,让我爱不释手。
如果你想将一个大集合分成若干个小集合。
之前我们是这样做的:
List<Integer> list = Lists.newArrayList(1, 2, 3, 4, 5);
List<List<Integer>> partitionList = Lists.newArrayList();
int size = 0;
List<Integer> dataList = Lists.newArrayList();
for(Integer data : list) {
if(size >= 2) {
dataList = Lists.newArrayList();
size = 0;
}
size++;
dataList.add(data);
}
将list按size=2分成多个小集合,上面的代码看起来比较麻烦。
如果使用Lists的partition方法,可以这样写代码:
List<Integer> list = Lists.newArrayList(1, 2, 3, 4, 5); List<List<Integer>> partitionList = Lists.partition(list, 2); System.out.println(partitionList);
执行结果:
[[1, 2], [3, 4], [5]]
这个例子中,list有5条数据,我将list集合按大小为2,分成了3页,即变成3个小集合。
这个是我最喜欢的方法之一,经常在项目中使用。
比如有个需求:现在有5000个id,需要调用批量用户查询接口,查出用户数据。但如果你直接查5000个用户,单次接口响应时间可能会非常慢。如果改成分页处理,每次只查500个用户,异步调用10次接口,就不会有单次接口响应慢的问题。
13.用同步代码块代替同步方法
在某些业务场景中,为了防止多个线程并发修改某个共享数据,造成数据异常。
为了解决并发场景下,多个线程同时修改数据,造成数据不一致的情况。通常情况下,我们会:加锁。
但如果锁加得不好,导致锁的粒度太粗,也会非常影响接口性能。
在java中提供了synchronized关键字给我们的代码加锁。
通常有两种写法:在方法上加锁 和 在代码块上加锁。
先看看如何在方法上加锁:
public synchronized doSave(String fileUrl) {
mkdir();
uploadFile(fileUrl);
sendMessage(fileUrl);
}
这里加锁的目的是为了防止并发的情况下,创建了相同的目录,第二次会创建失败,影响业务功能。
但这种直接在方法上加锁,锁的粒度有点粗。因为doSave方法中的上传文件和发消息方法,是不需要加锁的。只有创建目录方法,才需要加锁。
我们都知道文件上传操作是非常耗时的,如果将整个方法加锁,那么需要等到整个方法执行完之后才能释放锁。显然,这会导致该方法的性能很差,变得得不偿失。
这时,我们可以改成在代码块上加锁了,具体代码如下:
public void doSave(String path,String fileUrl) {
synchronized(this) {
if(!exists(path)) {
mkdir(path);
}
}
uploadFile(fileUrl);
sendMessage(fileUrl);
}
这样改造之后,锁的粒度一下子变小了,只有并发创建目录功能才加了锁。而创建目录是一个非常快的操作,即使加锁对接口的性能影响也不大。
最重要的是,其他的上传文件和发送消息功能,任然可以并发执行。
14.不用的数据及时清理
在Java中保证线程安全的技术有很多,可以使用synchroized、Lock等关键字给代码块加锁。
但是它们有个共同的特点,就是加锁会对代码的性能有一定的损耗。
其实,在jdk中还提供了另外一种思想即:用空间换时间。
没错,使用ThreadLocal类就是对这种思想的一种具体体现。
ThreadLocal为每个使用变量的线程提供了一个独立的变量副本,这样每一个线程都能独立地改变自己的副本,而不会影响其它线程所对应的副本。
ThreadLocal的用法大致是这样的:
- 先创建一个CurrentUser类,其中包含了ThreadLocal的逻辑。
public class CurrentUser {
private static final ThreadLocal<UserInfo> THREA_LOCAL = new ThreadLocal();
public static void set(UserInfo userInfo) {
THREA_LOCAL.set(userInfo);
}
public static UserInfo get() {
THREA_LOCAL.get();
}
public static void remove() {
THREA_LOCAL.remove();
}
}
- 在业务代码中调用CurrentUser类。
public void doSamething(UserDto userDto) {
UserInfo userInfo = convert(userDto);
CurrentUser.set(userInfo);
...
//业务代码
UserInfo userInfo = CurrentUser.get();
...
}
在业务代码的第一行,将userInfo对象设置到CurrentUser,这样在业务代码中,就能通过CurrentUser.get()获取到刚刚设置的userInfo对象。特别是对业务代码调用层级比较深的情况,这种用法非常有用,可以减少很多不必要传参。
但在高并发的场景下,这段代码有问题,只往ThreadLocal存数据,数据用完之后并没有及时清理。
ThreadLocal即使使用了WeakReference(弱引用)也可能会存在内存泄露问题,因为 entry对象中只把key(即threadLocal对象)设置成了弱引用,但是value值没有。
那么,如何解决这个问题呢?
public void doSamething(UserDto userDto) {
UserInfo userInfo = convert(userDto);
try{
CurrentUser.set(userInfo);
...
//业务代码
UserInfo userInfo = CurrentUser.get();
...
} finally {
CurrentUser.remove();
}
}
需要在finally代码块中,调用remove方法清理没用的数据。
15.用equals方法比较是否相等
不知道你在项目中有没有见过,有些同事对Integer类型的两个参数使用==号比较是否相等?
反正我见过的,那么这种用法对吗?
我的回答是看具体场景,不能说一定对,或不对。
有些状态字段,比如:orderStatus有:-1(未下单),0(已下单),1(已支付),2(已完成),3(取消),5种状态。
这时如果用==判断是否相等:
Integer orderStatus1 = new Integer(1); Integer orderStatus2 = new Integer(1); System.out.println(orderStatus1 == orderStatus2);
返回结果会是true吗?
答案:是false。
有些同学可能会反驳,Integer中不是有范围是:-128-127的缓存吗?
为什么是false?
先看看Integer的构造方法:
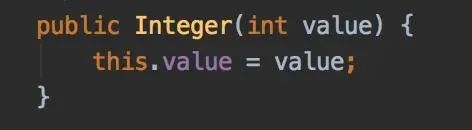
它其实并没有用到缓存。
那么缓存是在哪里用的?
答案在valueOf方法中:

如果上面的判断改成这样:
String orderStatus1 = new String("1");
String orderStatus2 = new String("1");
System.out.println(Integer.valueOf(orderStatus1) == Integer.valueOf(orderStatus2));
返回结果会是true吗?
答案:还真是true。
我们要养成良好编码习惯,尽量少用==判断两个Integer类型数据是否相等,只有在上述非常特殊的场景下才相等。
而应该改成使用equals方法判断:
Integer orderStatus1 = new Integer(1); Integer orderStatus2 = new Integer(1); System.out.println(orderStatus1.equals(orderStatus2));
运行结果为true。
16.避免创建大集合
很多时候,我们在日常开发中,需要创建集合。比如:为了性能考虑,从数据库查询某张表的所有数据,一次性加载到内存的某个集合中,然后做业务逻辑处理。
例如:
List<User> userList = userMapper.getAllUser();
for(User user:userList) {
doSamething();
}
从数据库一次性查询出所有用户,然后在循环中,对每个用户进行业务逻辑处理。
如果用户表的数据量非常多时,这样userList集合会很大,可能直接导致内存不足,而使整个应用挂掉。
针对这种情况,必须做分页处理。
例如:
private static final int PAGE_SIZE = 500;
int currentPage = 1;
RequestPage page = new RequestPage();
page.setPageNo(currentPage);
page.setPageSize(PAGE_SIZE);
Page<User> pageUser = userMapper.search(page);
while(pageUser.getPageCount() >= currentPage) {
for(User user:pageUser.getData()) {
doSamething();
}
page.setPageNo(++currentPage);
pageUser = userMapper.search(page);
}
通过上面的分页改造之后,每次从数据库中只查询500条记录,保存到userList集合中,这样userList不会占用太多的内存。
这里特别说明一下,如果你查询的表中的数据量本来就很少,一次性保存到内存中,也不会占用太多内存,这种情况也可以不做分页处理。
此外,还有中特殊的情况,即表中的记录数并算不多,但每一条记录,都有很多字段,单条记录就占用很多内存空间,这时也需要做分页处理,不然也会有问题。
整体的原则是要尽量避免创建大集合,导致内存不足的问题,但是具体多大才算大集合。目前没有一个唯一的衡量标准,需要结合实际的业务场景进行单独分析。
17.状态用枚举
在我们建的表中,有很多状态字段,比如:订单状态、禁用状态、删除状态等。
每种状态都有多个值,代表不同的含义。
比如订单状态有:
- 1:表示下单
- 2:表示支付
- 3:表示完成
- 4:表示撤销
如果没有使用枚举,一般是这样做的:
public static final int ORDER_STATUS_CREATE = 1; public static final int ORDER_STATUS_PAY = 2; public static final int ORDER_STATUS_DONE = 3; public static final int ORDER_STATUS_CANCEL = 4; public static final String ORDER_STATUS_CREATE_MESSAGE = "下单"; public static final String ORDER_STATUS_PAY = "下单"; public static final String ORDER_STATUS_DONE = "下单"; public static final String ORDER_STATUS_CANCEL = "下单";
需要定义很多静态常量,包含不同的状态和状态的描述。
使用枚举定义之后,代码如下:
public enum OrderStatusEnum {
CREATE(1, "下单"),
PAY(2, "支付"),
DONE(3, "完成"),
CANCEL(4, "撤销");
private int code;
private String message;
OrderStatusEnum(int code, String message) {
this.code = code;
this.message = message;
}
public int getCode() {
return this.code;
}
public String getMessage() {
return this.message;
}
public static OrderStatusEnum getOrderStatusEnum(int code) {
return Arrays.stream(OrderStatusEnum.values()).filter(x -> x.code == code).findFirst().orElse(null);
}
}
使用枚举改造之后,职责更单一了。
而且使用枚举的好处是:
- 代码的可读性变强了,不同的状态,有不同的枚举进行统一管理和维护。
- 枚举是天然单例的,可以直接使用==号进行比较。
- code和message可以成对出现,比较容易相关转换。
- 枚举可以消除if…else过多问题。
18.把固定值定义成静态常量
不知道你在实际的项目开发中,有没有使用过固定值?
例如:
if(user.getId() < 1000L) {
doSamething();
}
或者:
if(Objects.isNull(user)) {
throw new BusinessException("该用户不存在");
}
其中1000L和该用户不存在是固定值,每次都是一样的。
既然是固定值,我们为什么不把它们定义成静态常量呢?
这样语义上更直观,方便统一管理和维护,更方便代码复用。
代码优化为:
private static final int DEFAULT_USER_ID = 1000L;
...
if(user.getId() < DEFAULT_USER_ID) {
doSamething();
}
或者:
private static final String NOT_FOUND_MESSAGE = "该用户不存在";
...
if(Objects.isNull(user)) {
throw new BusinessException(NOT_FOUND_MESSAGE);
}
使用static final关键字修饰静态常量,static表示静态的意思,即类变量,而final表示不允许修改。
两个关键字加在一起,告诉Java虚拟机这种变量,在内存中只有一份,在全局上是唯一的,不能修改,也就是静态常量。
19.避免大事务
很多小伙伴在使用spring框架开发项目时,为了方便,喜欢使用@Transactional注解提供事务功能。
没错,使用@Transactional注解这种声明式事务的方式提供事务功能,确实能少写很多代码,提升开发效率。
但也容易造成大事务,引发其他的问题。
下面用一张图看看大事务引发的问题。
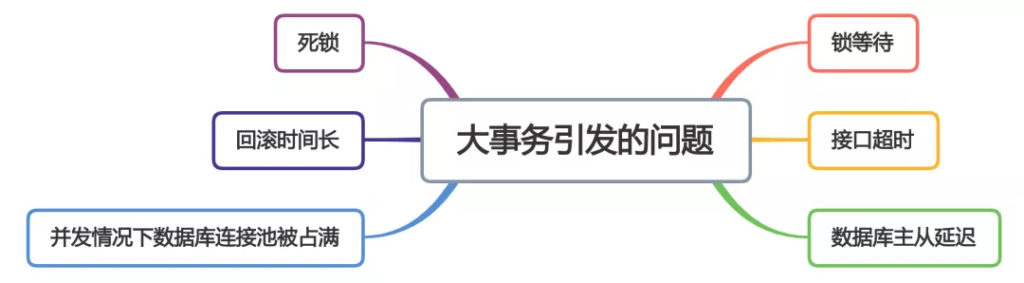
从图中能够看出,大事务问题可能会造成接口超时,对接口的性能有直接的影响。
我们该如何优化大事务呢?
- 少用@Transactional注解
- 将查询(select)方法放到事务外
- 事务中避免远程调用
- 事务中避免一次性处理太多数据
- 有些功能可以非事务执行
- 有些功能可以异步处理
20.消除过长的if…else
我们在写代码的时候,if…else的判断条件是必不可少的。不同的判断条件,走的代码逻辑通常会不一样。
废话不多说,先看看下面的代码。
public interface IPay {
void pay();
}
@Service
public class AliaPay implements IPay {
@Override
public void pay() {
System.out.println("===发起支付宝支付===");
}
}
@Service
public class WeixinPay implements IPay {
@Override
public void pay() {
System.out.println("===发起微信支付===");
}
}
@Service
public class JingDongPay implements IPay {
@Override
public void pay() {
System.out.println("===发起京东支付===");
}
}
@Service
public class PayService {
@Autowired
private AliaPay aliaPay;
@Autowired
private WeixinPay weixinPay;
@Autowired
private JingDongPay jingDongPay;
public void toPay(String code) {
if ("alia".equals(code)) {
aliaPay.pay();
} elseif ("weixin".equals(code)) {
weixinPay.pay();
} elseif ("jingdong".equals(code)) {
jingDongPay.pay();
} else {
System.out.println("找不到支付方式");
}
}
}
PayService类的toPay方法主要是为了发起支付,根据不同的code,决定调用用不同的支付类(比如:aliaPay)的pay方法进行支付。
这段代码有什么问题呢?也许有些人就是这么干的。
试想一下,如果支付方式越来越多,比如:又加了百度支付、美团支付、银联支付等等,就需要改toPay方法的代码,增加新的else…if判断,判断多了就会导致逻辑越来越多?
很明显,这里违法了设计模式六大原则的:开闭原则 和 单一职责原则。
开闭原则:对扩展开放,对修改关闭。就是说增加新功能要尽量少改动已有代码。
单一职责原则:顾名思义,要求逻辑尽量单一,不要太复杂,便于复用。
那么,如何优化if…else判断呢?
答:使用 策略模式+工厂模式。
策略模式定义了一组算法,把它们一个个封装起来, 并且使它们可相互替换。工厂模式用于封装和管理对象的创建,是一种创建型模式。
public interface IPay {
void pay();
}
@Service
public class AliaPay implements IPay {
@PostConstruct
public void init() {
PayStrategyFactory.register("aliaPay", this);
}
@Override
public void pay() {
System.out.println("===发起支付宝支付===");
}
}
@Service
public class WeixinPay implements IPay {
@PostConstruct
public void init() {
PayStrategyFactory.register("weixinPay", this);
}
@Override
public void pay() {
System.out.println("===发起微信支付===");
}
}
@Service
public class JingDongPay implements IPay {
@PostConstruct
public void init() {
PayStrategyFactory.register("jingDongPay", this);
}
@Override
public void pay() {
System.out.println("===发起京东支付===");
}
}
public class PayStrategyFactory {
private static Map<String, IPay> PAY_REGISTERS = new HashMap<>();
public static void register(String code, IPay iPay) {
if (null != code && !"".equals(code)) {
PAY_REGISTERS.put(code, iPay);
}
}
public static IPay get(String code) {
return PAY_REGISTERS.get(code);
}
}
@Service
public class PayService3 {
public void toPay(String code) {
PayStrategyFactory.get(code).pay();
}
}
这段代码的关键是PayStrategyFactory类,它是一个策略工厂,里面定义了一个全局的map,在所有IPay的实现类中注册当前实例到map中,然后在调用的地方通过PayStrategyFactory类根据code从map获取支付类实例即可。
如果加了一个新的支付方式,只需新加一个类实现IPay接口,定义init方法,并且重写pay方法即可,其他代码基本上可以不用动。
21.防止死循环
有些小伙伴看到这个标题,可能会感到有点意外,代码中不是应该避免死循环吗?为啥还是会产生死循环?
殊不知有些死循环是我们自己写的,例如下面这段代码:
while(true) {
if(condition) {
break;
}
System.out.println("do samething");
}
这里使用了while(true)的循环调用,这种写法在CAS自旋锁中使用比较多。
当满足condition等于true的时候,则自动退出该循环。
如果condition条件非常复杂,一旦出现判断不正确,或者少写了一些逻辑判断,就可能在某些场景下出现死循环的问题。
出现死循环,大概率是开发人员人为的bug导致的,不过这种情况很容易被测出来。
还有一种隐藏的比较深的死循环,是由于代码写的不太严谨导致的。如果用正常数据,可能测不出问题,但一旦出现异常数据,就会立即出现死循环。
其实,还有另一种死循环:无限递归。
如果想要打印某个分类的所有父分类,可以用类似这样的递归方法实现:
public void printCategory(Category category) {
if(category == null
|| category.getParentId() == null) {
return;
}
System.out.println("父分类名称:"+ category.getName());
Category parent = categoryMapper.getCategoryById(category.getParentId());
printCategory(parent);
}
正常情况下,这段代码是没有问题的。
但如果某次有人误操作,把某个分类的parentId指向了它自己,这样就会出现无限递归的情况。导致接口一直不能返回数据,最终会发生堆栈溢出。
建议写递归方法时,设定一个递归的深度,比如:分类最大等级有4级,则深度可以设置为4。然后在递归方法中做判断,如果深度大于4时,则自动返回,这样就能避免无限循环的情况。
22.注意BigDecimal的坑
通常我们会把一些小数类型的字段(比如:金额),定义成BigDecimal,而不是Double,避免丢失精度问题。
使用Double时可能会有这种场景:
double amount1 = 0.02; double amount2 = 0.03; System.out.println(amount2 - amount1);
正常情况下预计amount2 – amount1应该等于0.01
但是执行结果,却为:
0.009999999999999998
实际结果小于预计结果。
Double类型的两个参数相减会转换成二进制,因为Double有效位数为16位这就会出现存储小数位数不够的情况,这种情况下就会出现误差。
常识告诉我们使用BigDecimal能避免丢失精度。
但是使用BigDecimal能避免丢失精度吗?
答案是否定的。
为什么?
BigDecimal amount1 = new BigDecimal(0.02); BigDecimal amount2 = new BigDecimal(0.03); System.out.println(amount2.subtract(amount1));
这个例子中定义了两个BigDecimal类型参数,使用构造函数初始化数据,然后打印两个参数相减后的值。
结果:
0.0099999999999999984734433411404097569175064563751220703125
不科学呀,为啥还是丢失精度了?
Jdk中BigDecimal的构造方法上有这样一段描述:
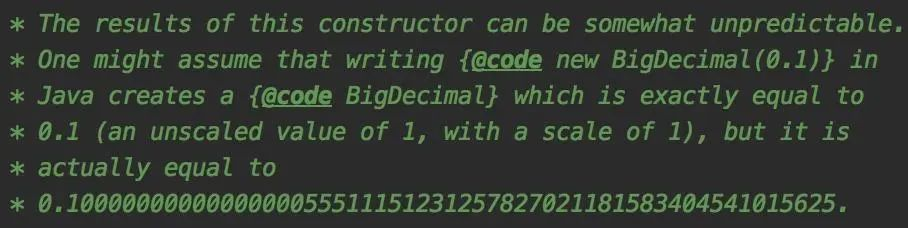
大致的意思是此构造函数的结果可能不可预测,可能会出现创建时为0.1,但实际是0.1000000000000000055511151231257827021181583404541015625的情况。
由此可见,使用BigDecimal构造函数初始化对象,也会丢失精度。
那么,如何才能不丢失精度呢?
BigDecimal amount1 = new BigDecimal(Double.toString(0.02)); BigDecimal amount2 = new BigDecimal(Double.toString(0.03)); System.out.println(amount2.subtract(amount1));
我们可以使用Double.toString方法,对double类型的小数进行转换,这样能保证精度不丢失。
其实,还有更好的办法:
BigDecimal amount1 = BigDecimal.valueOf(0.02); BigDecimal amount2 = BigDecimal.valueOf(0.03); System.out.println(amount2.subtract(amount1));
使用BigDecimal.valueOf方法初始化BigDecimal类型参数,也能保证精度不丢失。在新版的阿里巴巴开发手册中,也推荐使用这种方式创建BigDecimal参数。
23.尽可能复用代码
ctrl + c 和 ctrl + v可能是程序员使用最多的快捷键了。
没错,我们是大自然的搬运工。哈哈哈。
在项目初期,我们使用这种工作模式,确实可以提高一些工作效率,可以少写(实际上是少敲)很多代码。
但它带来的问题是:会出现大量的代码重复。例如:
@Service
@Slf4j
public class TestService1 {
public void test1() {
addLog("test1");
}
private void addLog(String info) {
if (log.isInfoEnabled()) {
log.info("info:{}", info);
}
}
}
@Service
@Slf4j
public class TestService2 {
public void test2() {
addLog("test2");
}
private void addLog(String info) {
if (log.isInfoEnabled()) {
log.info("info:{}", info);
}
}
}
@Service
@Slf4j
public class TestService3 {
public void test3() {
addLog("test3");
}
private void addLog(String info) {
if (log.isInfoEnabled()) {
log.info("info:{}", info);
}
}
}
在TestService1、TestService2、TestService3类中,都有一个addLog方法用于添加日志。
本来该功能用得好好的,直到有一天,线上出现了一个事故:服务器磁盘满了。
原因是打印的日志太多,记了很多没必要的日志,比如:查询接口的所有返回值,大对象的具体打印等。
没办法,只能将addLog方法改成只记录debug日志。
于是乎,你需要全文搜索,addLog方法去修改,改成如下代码:
private void addLog(String info) {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("debug:{}", info);
}
}
这里是有三个类中需要修改这段代码,但如果实际工作中有三十个、三百个类需要修改,会让你非常痛苦。改错了,或者改漏了,都会埋下隐患,把自己坑了。
为何不把这种功能的代码提取出来,放到某个工具类中呢?
@Slf4j
public class LogUtil {
private LogUtil() {
throw new RuntimeException("初始化失败");
}
public static void addLog(String info) {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("debug:{}", info);
}
}
}
然后,在其他的地方,只需要调用。
@Service
@Slf4j
public class TestService1 {
public void test1() {
LogUtil.addLog("test1");
}
}
如果哪天addLog的逻辑又要改了,只需要修改LogUtil类的addLog方法即可。你可以自信满满的修改,不需要再小心翼翼了。
我们写的代码,绝大多数是可维护性的代码,而非一次性的。所以,建议在写代码的过程中,如果出现重复的代码,尽量提取成公共方法。千万别因为项目初期一时的爽快,而给项目埋下隐患,后面的维护成本可能会非常高。
24.foreach循环中不remove元素
我们知道在Java中,循环有很多种写法,比如:while、for、foreach等。
public class Test2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> list = Lists.newArrayList("a","b","c");
for (String temp : list) {
if ("c".equals(temp)) {
list.remove(temp);
}
}
System.out.println(list);
}
}
执行结果:
Exception in thread "main" java.util.ConcurrentModificationException at java.util.ArrayList$Itr.checkForComodification(ArrayList.java:901) at java.util.ArrayList$Itr.next(ArrayList.java:851) at com.sue.jump.service.test1.Test2.main(Test2.java:24)
这种在foreach循环中调用remove方法删除元素,可能会报ConcurrentModificationException异常。
如果想在遍历集合时,删除其中的元素,可以用for循环,例如:
public class Test2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> list = Lists.newArrayList("a","b","c");
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
String temp = list.get(i);
if ("c".equals(temp)) {
list.remove(temp);
}
}
System.out.println(list);
}
}
执行结果:
[a, b]
25.避免随意打印日志
在我们写代码的时候,打印日志是必不可少的工作之一。
因为日志可以帮我们快速定位问题,判断代码当时真正的执行逻辑。
但打印日志的时候也需要注意,不是说任何时候都要打印日志,比如:
@PostMapping("/query")
public List<User> query(@RequestBody List<Long> ids) {
log.info("request params:{}", ids);
List<User> userList = userService.query(ids);
log.info("response:{}", userList);
return userList;
}
对于有些查询接口,在日志中打印出了请求参数和接口返回值。
咋一看没啥问题。
但如果ids中传入值非常多,比如有1000个。而该接口被调用的频次又很高,一下子就会打印大量的日志,用不了多久就可能把磁盘空间打满。
如果真的想打印这些日志该怎么办?
@PostMapping("/query")
public List<User> query(@RequestBody List<Long> ids) {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("request params:{}", ids);
}
List<User> userList = userService.query(ids);
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("response:{}", userList);
}
return userList;
}
使用isDebugEnabled判断一下,如果当前的日志级别是debug才打印日志。生产环境默认日志级别是info,在有些紧急情况下,把某个接口或者方法的日志级别改成debug,打印完我们需要的日志后,又调整回去。
方便我们定位问题,又不会产生大量的垃圾日志,一举两得。
26.比较时把常量写前面
在比较两个参数值是否相等时,通常我们会使用==号,或者equals方法。
我在第15章节中说过,使用==号比较两个值是否相等时,可能会存在问题,建议使用equals方法做比较。
反例:
if(user.getName().equals("苏三")) {
System.out.println("找到:"+user.getName());
}
在上面这段代码中,如果user对象,或者user.getName()方法返回值为null,则都报NullPointerException异常。
那么,如何避免空指针异常呢?
正例:
private static final String FOUND_NAME = "苏三";
...
if(null == user) {
return;
}
if(FOUND_NAME.equals(user.getName())) {
System.out.println("找到:"+user.getName());
}
在使用equals做比较时,尽量将常量写在前面,即equals方法的左边。
这样即使user.getName()返回的数据为null,equals方法会直接返回false,而不再是报空指针异常。
27.名称要见名知意
java中没有强制规定参数、方法、类或者包名该怎么起名。但如果我们没有养成良好的起名习惯,随意起名的话,可能会出现很多奇怪的代码。
27.1 有意义的参数名
有时候,我们写代码时为了省事(可以少敲几个字母),参数名起得越简单越好。假如同事A写的代码如下:
int a = 1; int b = 2; String c = "abc"; boolean b = false;
一段时间之后,同事A离职了,同事B接手了这段代码。
他此时一脸懵逼,a是什么意思,b又是什么意思,还有c…然后心里一万个草泥马。
给参数起一个有意义的名字,是非常重要的事情,避免给自己或者别人埋坑。
正解:
int supplierCount = 1; int purchaserCount = 2; String userName = "abc"; boolean hasSuccess = false;
27.2 见名知意
光起有意义的参数名还不够,我们不能就这点追求。我们起的参数名称最好能够见名知意,不然就会出现这样的情况:
String yongHuMing = "苏三"; String 用户Name = "苏三"; String su3 = "苏三"; String suThree = "苏三";
这几种参数名看起来是不是有点怪怪的?
为啥不定义成国际上通用的(地球人都能看懂)英文单词呢?
String userName = "苏三"; String susan = "苏三";
上面的这两个参数名,基本上大家都能看懂,减少了好多沟通成本。
所以建议在定义不管是参数名、方法名、类名时,优先使用国际上通用的英文单词,更简单直观,减少沟通成本。少用汉子、拼音,或者数字定义名称。
27.3 参数名风格一致
参数名其实有多种风格,列如:
//字母全小写 int suppliercount = 1; //字母全大写 int SUPPLIERCOUNT = 1; //小写字母 + 下划线 int supplier_count = 1; //大写字母 + 下划线 int SUPPLIER_COUNT = 1; //驼峰标识 int supplierCount = 1;
如果某个类中定义了多种风格的参数名称,看起来是不是有点杂乱无章?
所以建议类的成员变量、局部变量和方法参数使用supplierCount,这种驼峰风格,即:第一个字母小写,后面的每个单词首字母大写。例如:
int supplierCount = 1;
此外,为了好做区分,静态常量建议使用SUPPLIER_COUNT,即:大写字母 + 下划线分隔的参数名。例如:
private static final int SUPPLIER_COUNT = 1;
28.SimpleDateFormat线程不安全
在java8之前,我们对时间的格式化处理,一般都是用的SimpleDateFormat类实现的。例如:
@Service
public class SimpleDateFormatService {
public Date time(String time) throws ParseException {
SimpleDateFormat dateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
return dateFormat.parse(time);
}
}
如果你真的这样写,是没问题的。
就怕哪天抽风,你觉得dateFormat是一段固定的代码,应该要把它抽取成常量。
于是把代码改成下面的这样:
@Service
public class SimpleDateFormatService {
private static SimpleDateFormat dateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
public Date time(String time) throws ParseException {
return dateFormat.parse(time);
}
}
dateFormat对象被定义成了静态常量,这样就能被所有对象共用。
如果只有一个线程调用time方法,也不会出现问题。
但Serivce类的方法,往往是被Controller类调用的,而Controller类的接口方法,则会被tomcat的线程池调用。换句话说,可能会出现多个线程调用同一个Controller类的同一个方法,也就是会出现多个线程会同时调用time方法。
而time方法会调用SimpleDateFormat类的parse方法:
@Override
public Date parse(String text, ParsePosition pos) {
...
Date parsedDate;
try {
parsedDate = calb.establish(calendar).getTime();
...
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
pos.errorIndex = start;
pos.index = oldStart;
return null;
}
return parsedDate;
}
该方法会调用establish方法:
Calendar establish(Calendar cal) {
...
//1.清空数据
cal.clear();
//2.设置时间
cal.set(...);
//3.返回
return cal;
}
其中的步骤1、2、3是非原子操作。
但如果cal对象是局部变量还好,坏就坏在parse方法调用establish方法时,传入的calendar是SimpleDateFormat类的父类DateFormat的成员变量:
public abstract class DateFormat extends Forma {
....
protected Calendar calendar;
...
}
这样就可能会出现多个线程,同时修改同一个对象即:dateFormat,它的同一个成员变量即:Calendar值的情况。
这样可能会出现,某个线程设置好了时间,又被其他的线程修改了,从而出现时间错误的情况。
那么,如何解决这个问题呢?
- SimpleDateFormat类的对象不要定义成静态的,可以改成方法的局部变量。
- 使用ThreadLocal保存SimpleDateFormat类的数据。
- 使用java8的DateTimeFormatter类。
29.少用Executors创建线程池
我们都知道JDK5之后,提供了ThreadPoolExecutor类,用它可以自定义线程池。
线程池的好处有很多,下面主要说说这3个方面。
降低资源消耗:避免了频繁的创建线程和销毁线程,可以直接复用已有线程。而我们都知道,创建线程是非常耗时的操作。提供速度:任务过来之后,因为线程已存在,可以拿来直接使用。提高线程的可管理性:线程是非常宝贵的资源,如果创建过多的线程,不仅会消耗系统资源,甚至会影响系统的稳定。使用线程池,可以非常方便的创建、管理和监控线程。
当然JDK为了我们使用更便捷,专门提供了:Executors类,给我们快速创建线程池。
该类中包含了很多静态方法:
newCachedThreadPool:创建一个可缓冲的线程,如果线程池大小超过处理需要,可灵活回收空闲线程,若无可回收,则新建线程。newFixedThreadPool:创建一个固定大小的线程池,如果任务数量超过线程池大小,则将多余的任务放到队列中。newScheduledThreadPool:创建一个固定大小,并且能执行定时周期任务的线程池。newSingleThreadExecutor:创建只有一个线程的线程池,保证所有的任务安装顺序执行。
在高并发的场景下,如果大家使用这些静态方法创建线程池,会有一些问题。
那么,我们一起看看有哪些问题?
newFixedThreadPool:允许请求的队列长度是Integer.MAX_VALUE,可能会堆积大量的请求,从而导致OOM。newSingleThreadExecutor:允许请求的队列长度是Integer.MAX_VALUE,可能会堆积大量的请求,从而导致OOM。newCachedThreadPool:允许创建的线程数是Integer.MAX_VALUE,可能会创建大量的线程,从而导致OOM。
那我们该怎办呢?
优先推荐使用ThreadPoolExecutor类,我们自定义线程池。
具体代码如下:
ExecutorService threadPool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(
8, //corePoolSize线程池中核心线程数
10, //maximumPoolSize 线程池中最大线程数
60, //线程池中线程的最大空闲时间,超过这个时间空闲线程将被回收
TimeUnit.SECONDS,//时间单位
new ArrayBlockingQueue(500), //队列
new ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy()); //拒绝策略
顺便说一下,如果是一些低并发场景,使用Executors类创建线程池也未尝不可,也不能完全一棍子打死。在这些低并发场景下,很难出现OOM问题,所以我们需要根据实际业务场景选择。
30.Arrays.asList转换的集合别修改
在我们日常工作中,经常需要把数组转换成List集合。
因为数组的长度是固定的,不太好扩容,而List的长度是可变的,它的长度会根据元素的数量动态扩容。
在JDK的Arrays类中提供了asList方法,可以把数组转换成List。
正例:
String [] array = new String [] {"a","b","c"};
List<String> list = Arrays.asList(array);
for (String str : list) {
System.out.println(str);
}
在这个例子中,使用Arrays.asList方法将array数组,直接转换成了list。然后在for循环中遍历list,打印出它里面的元素。
如果转换后的list,只是使用,没新增或修改元素,不会有问题。
反例:
String[] array = new String[]{"a", "b", "c"};
List<String> list = Arrays.asList(array);
list.add("d");
for (String str : list) {
System.out.println(str);
}
执行结果:
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.UnsupportedOperationException at java.util.AbstractList.add(AbstractList.java:148) at java.util.AbstractList.add(AbstractList.java:108) at com.sue.jump.service.test1.Test2.main(Test2.java:24)
会直接报UnsupportedOperationException异常。
为什么呢?
答:使用Arrays.asList方法转换后的ArrayList,是Arrays类的内部类,并非java.util包下我们常用的ArrayList。
Arrays类的内部ArrayList类,它没有实现父类的add和remove方法,用的是父类AbstractList的默认实现。
我们看看AbstractList是如何实现的:
public void add(int index, E element) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
public E remove(int index) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
该类的add和remove方法直接抛异常了,因此调用Arrays类的内部ArrayList类的add和remove方法,同样会抛异常。
说实话,Java代码优化是一个比较大的话题,它里面可以优化的点非常多,我没办法一一列举完。在这里只能抛砖引玉,介绍一下比较常见的知识点,更全面的内容,需要小伙伴们自己去思考和探索。
引用自:https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/tw4lD0XA67yJKAwIWVicIQ